A Lightweight Multi-Scale Refinement Network for Gastrointestinal Disease Classification
Paper
Code
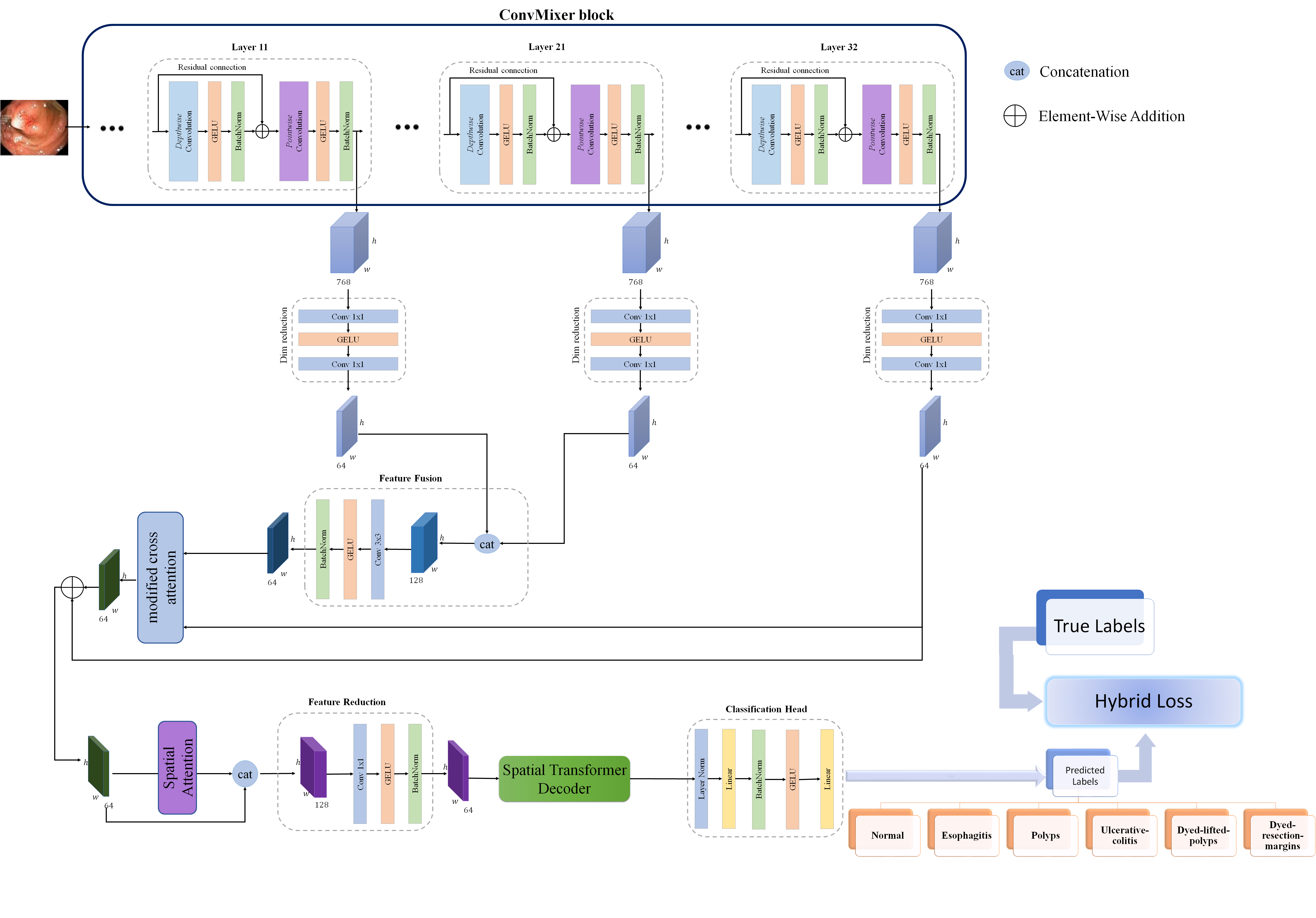
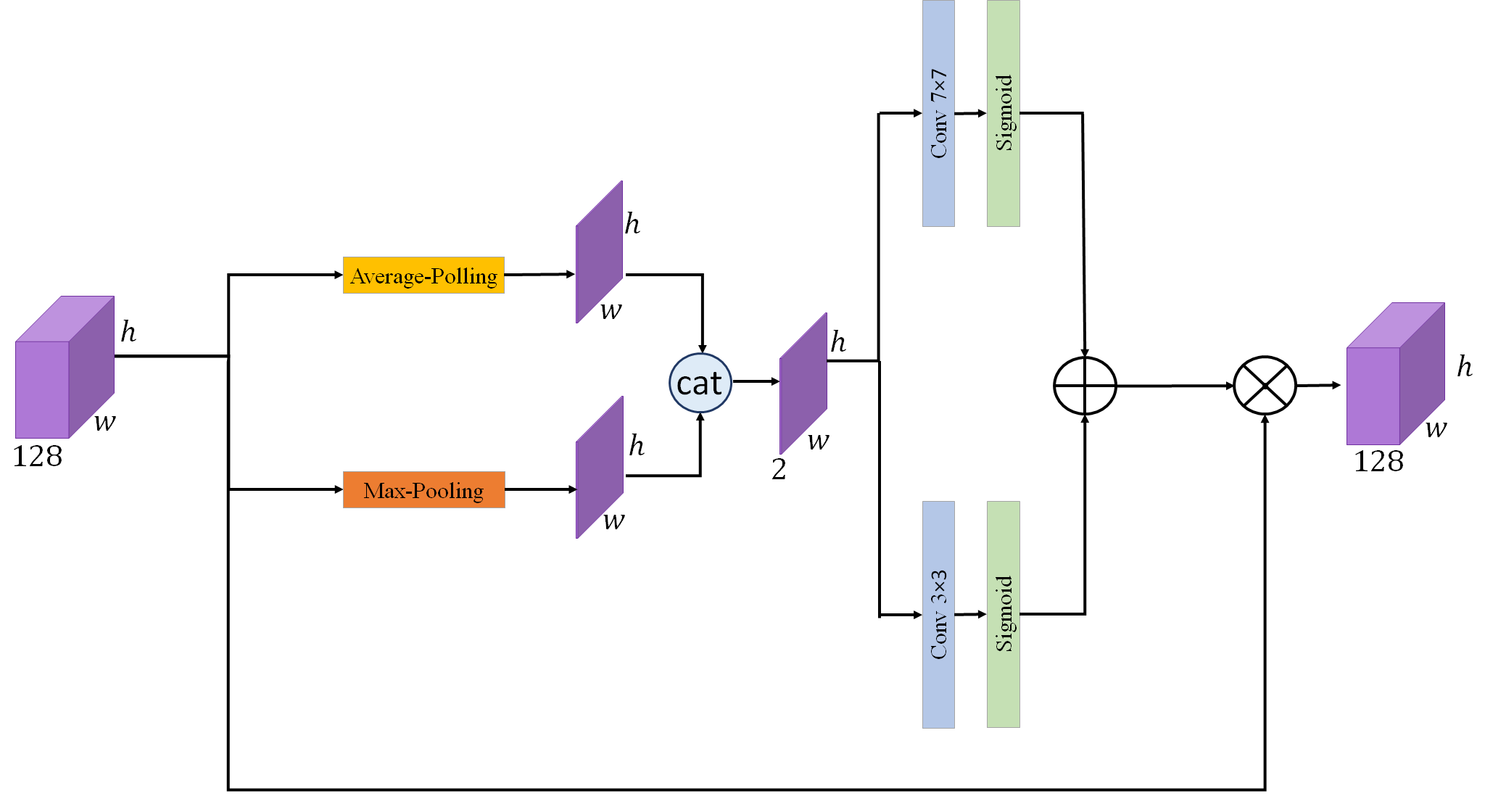
We present a lightweight deep learning architecture for gastrointestinal (GI) disease classification using endoscopic images. Our model used a frozen ConvMixer backbone
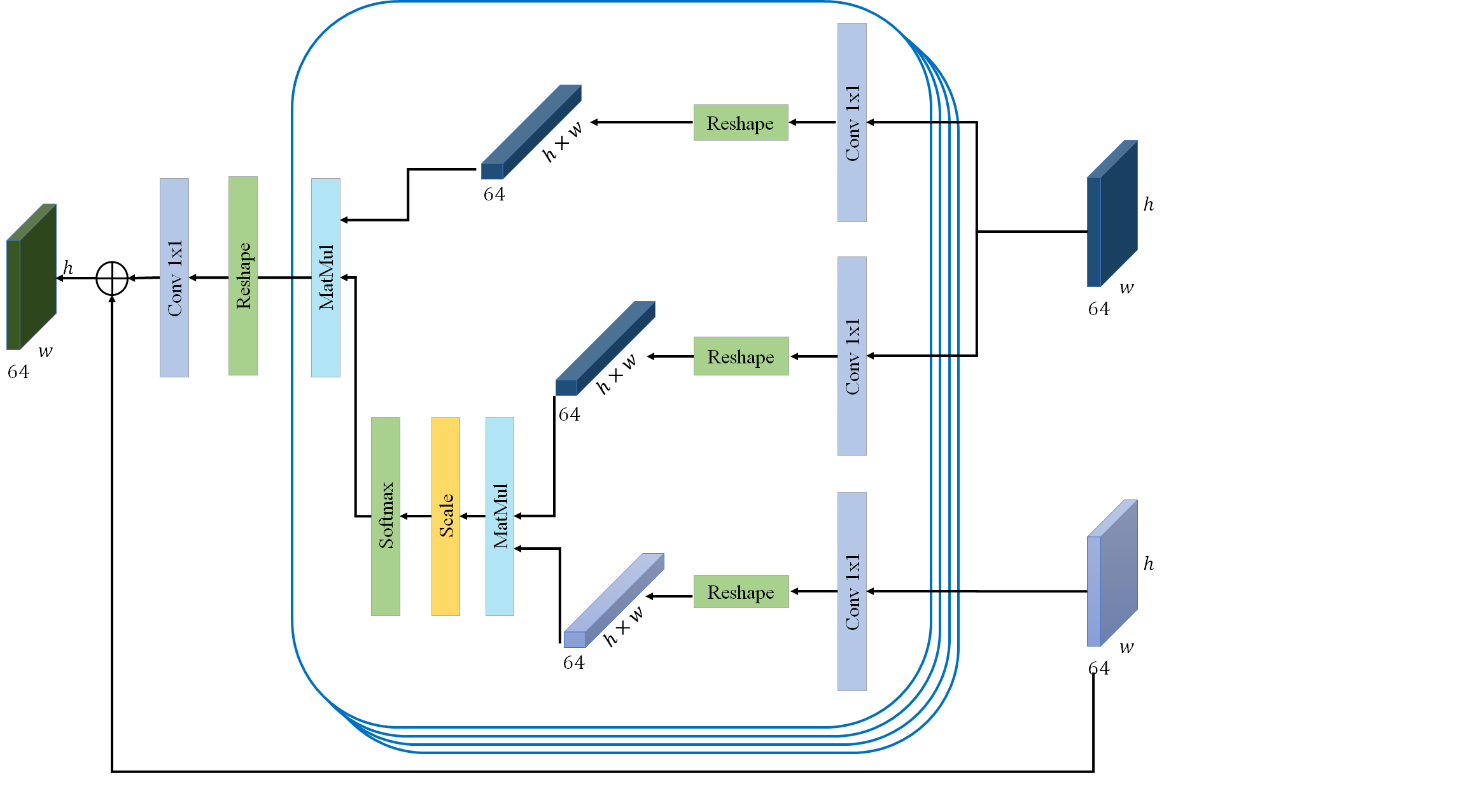
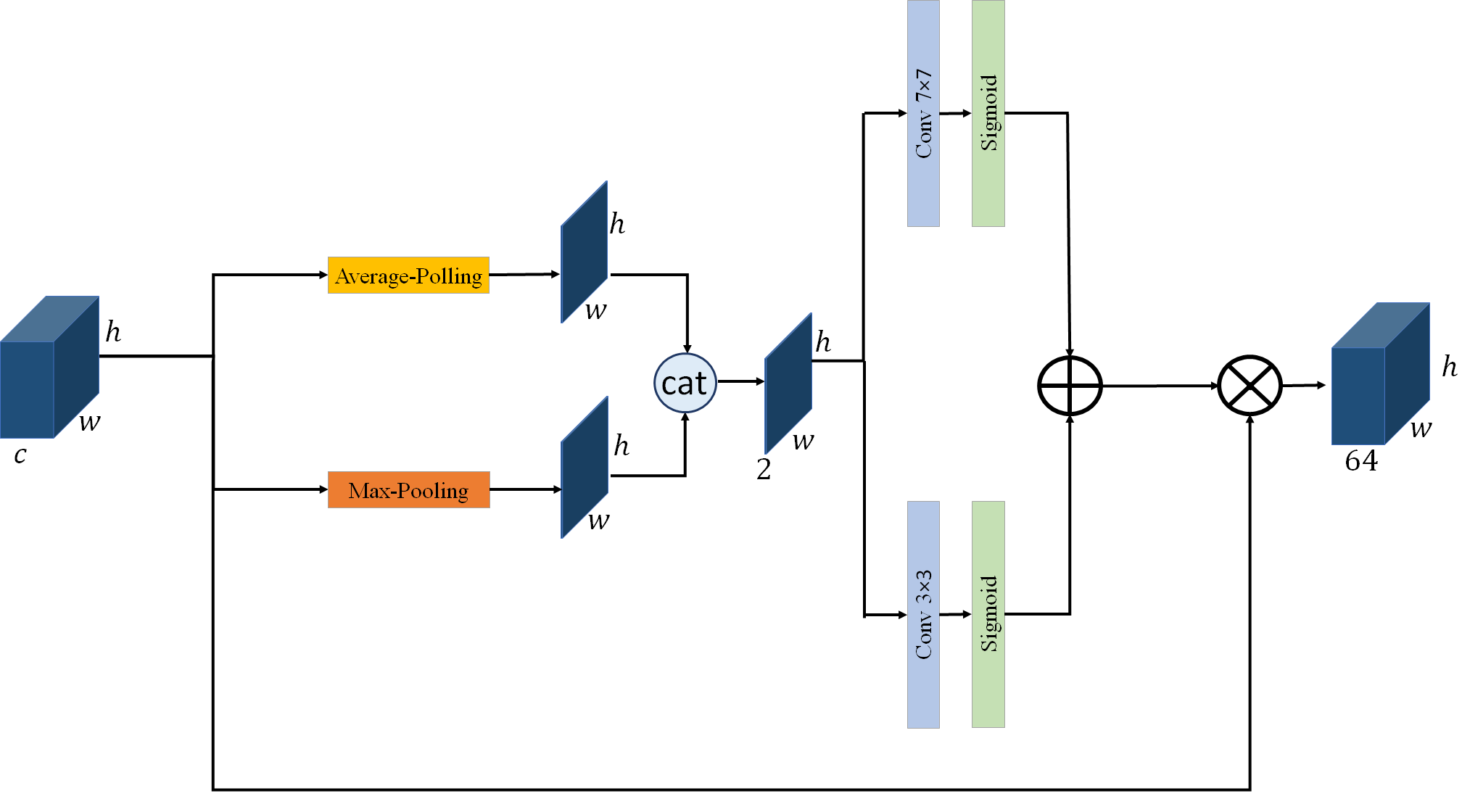
for multi-scale feature extraction, enhanced with modified attention mechanisms and a Transformer for refined discriminative feature learning. Explainable AI techniques are
integrated to improve reliability and interpretability, particularly for clinical applications. Evaluated on six benchmark GI datasets such as Kvasir-v1, GastroVision, Kvasir-Capsule,
Hyper-Kvasir, WCEBleedGen, and Kvasir-v2. our method achieves high accuracy (93.67%, 81.12%, 98.75%, 89.18%, 99.62%, and 93.33%, respectively) while remaining extremely parameter-efficient (0.38M),
demonstrating both its precision and lightweight design.
Efficient and Accurate Pneumonia Detection Using a Novel Multi-Scale Transformer Approach
Paper
Code
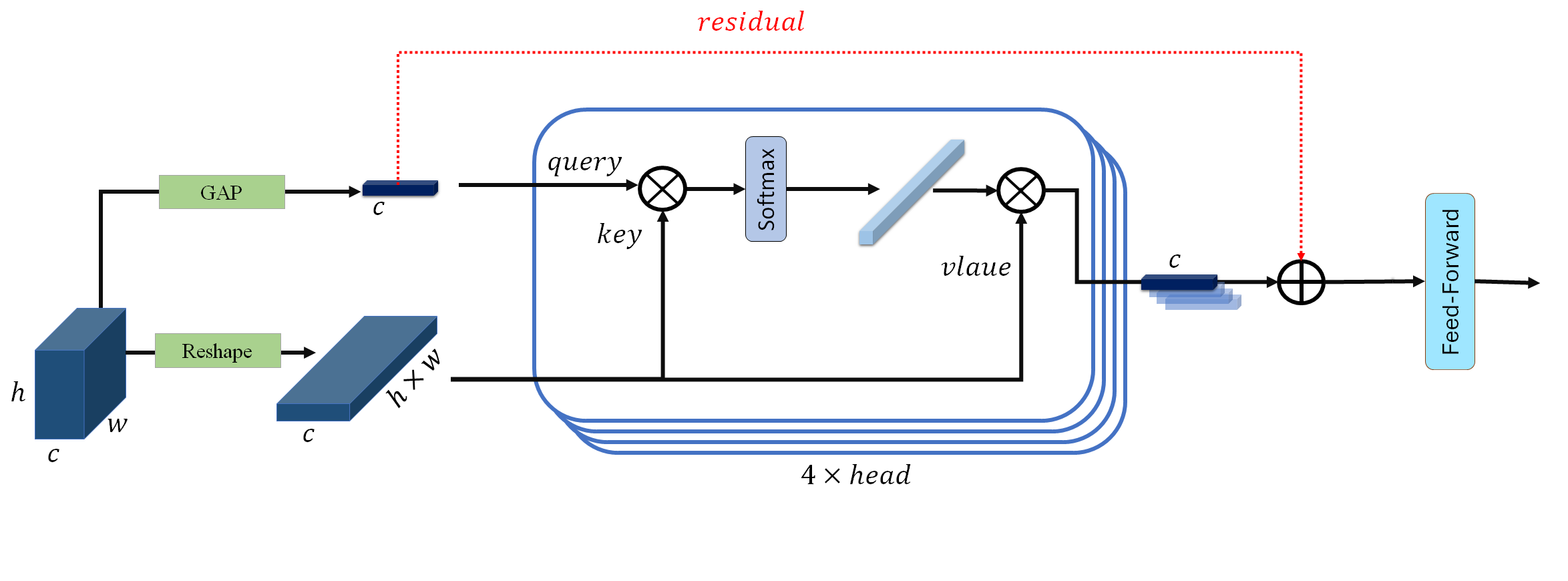
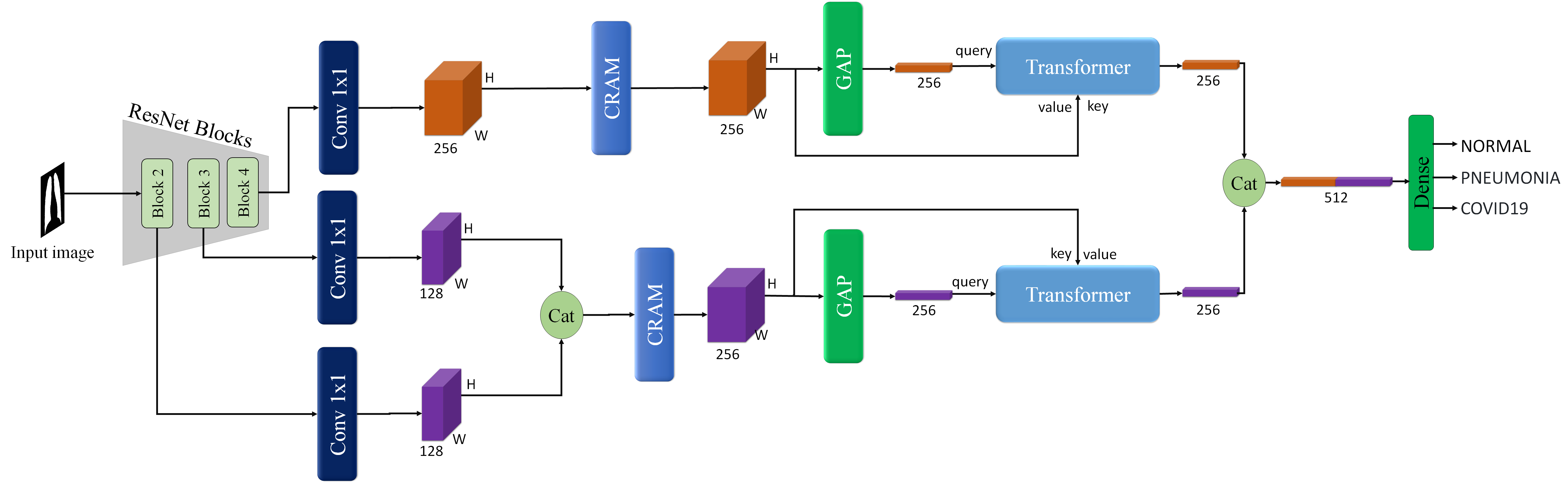
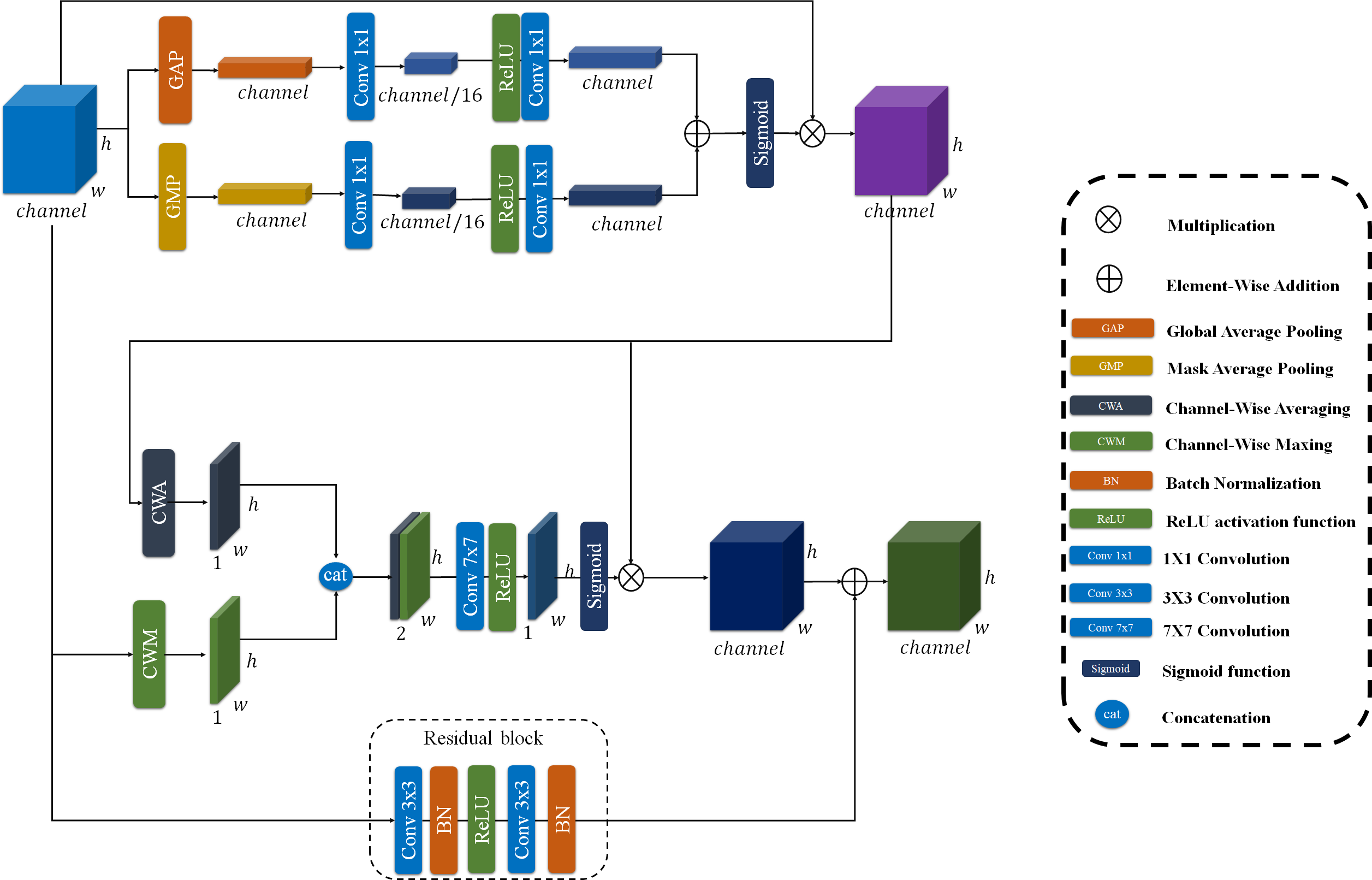
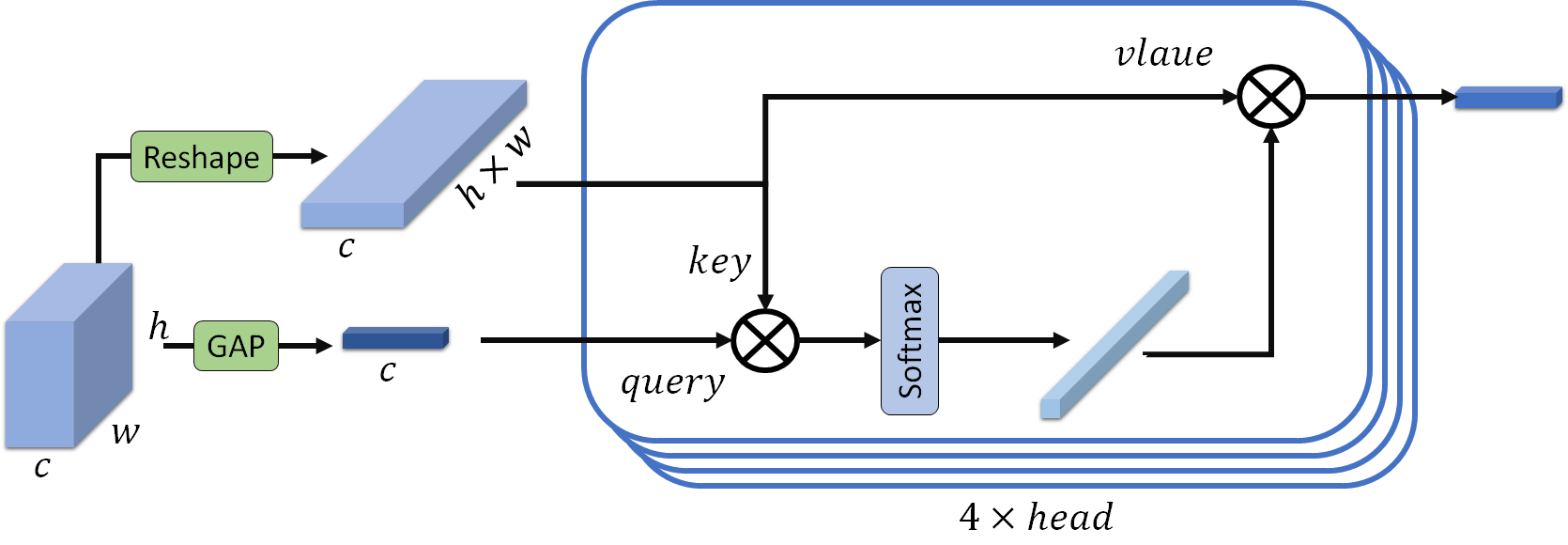
We propose a novel multi-scale transformer framework for pneumonia detection that integrates precise lung segmentation and classification.
Using a lightweight transformer-enhanced TransUNet for lung segmentation and pre-trained ResNet backbones for feature extraction,
combined with Residual Attention and modified transformer modules,
our method achieves robust performance with high accuracy (93.75% on Kermany, 96.04% on Cohen) while remaining computationally efficient
for resource-constrained clinical environments.
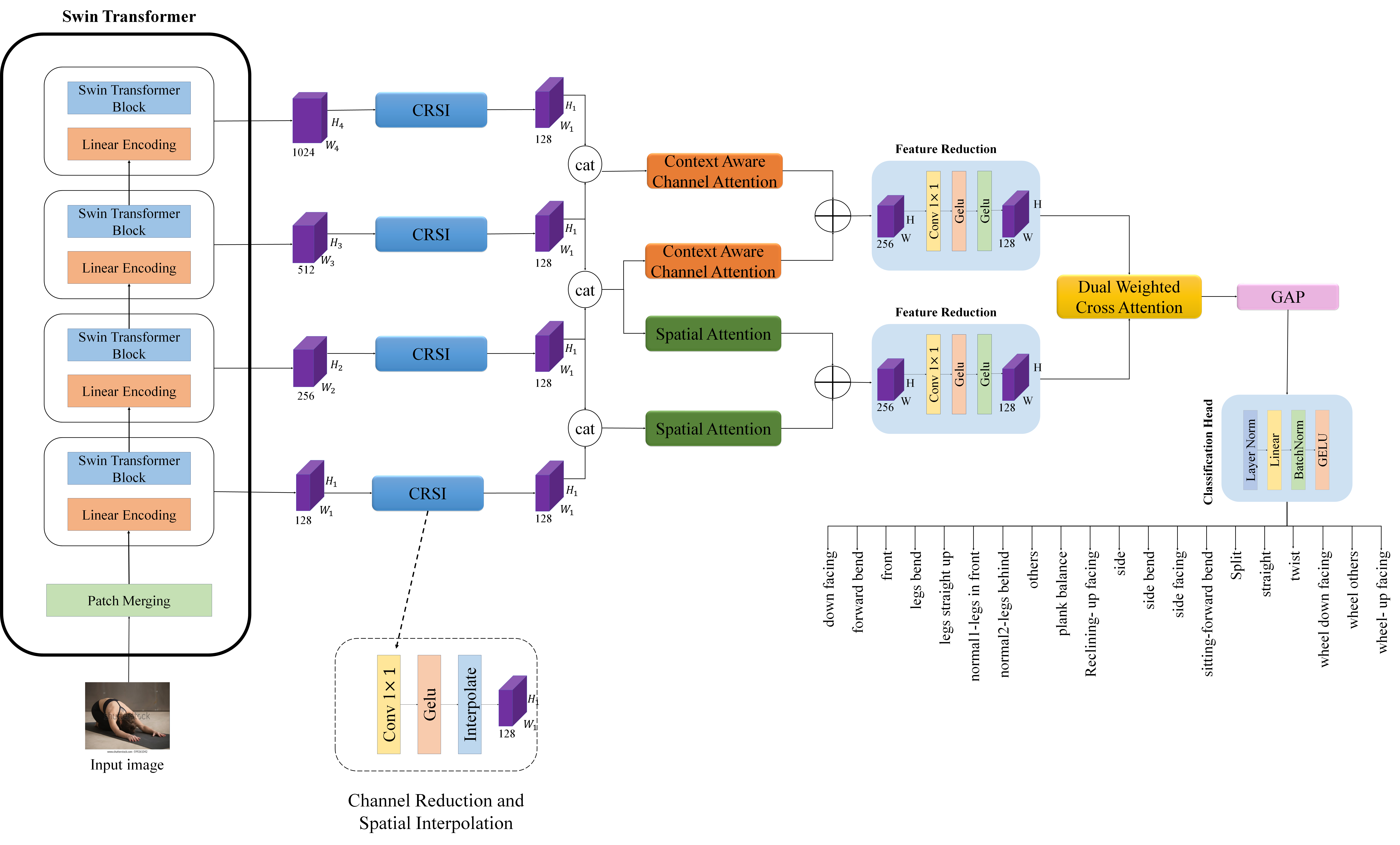
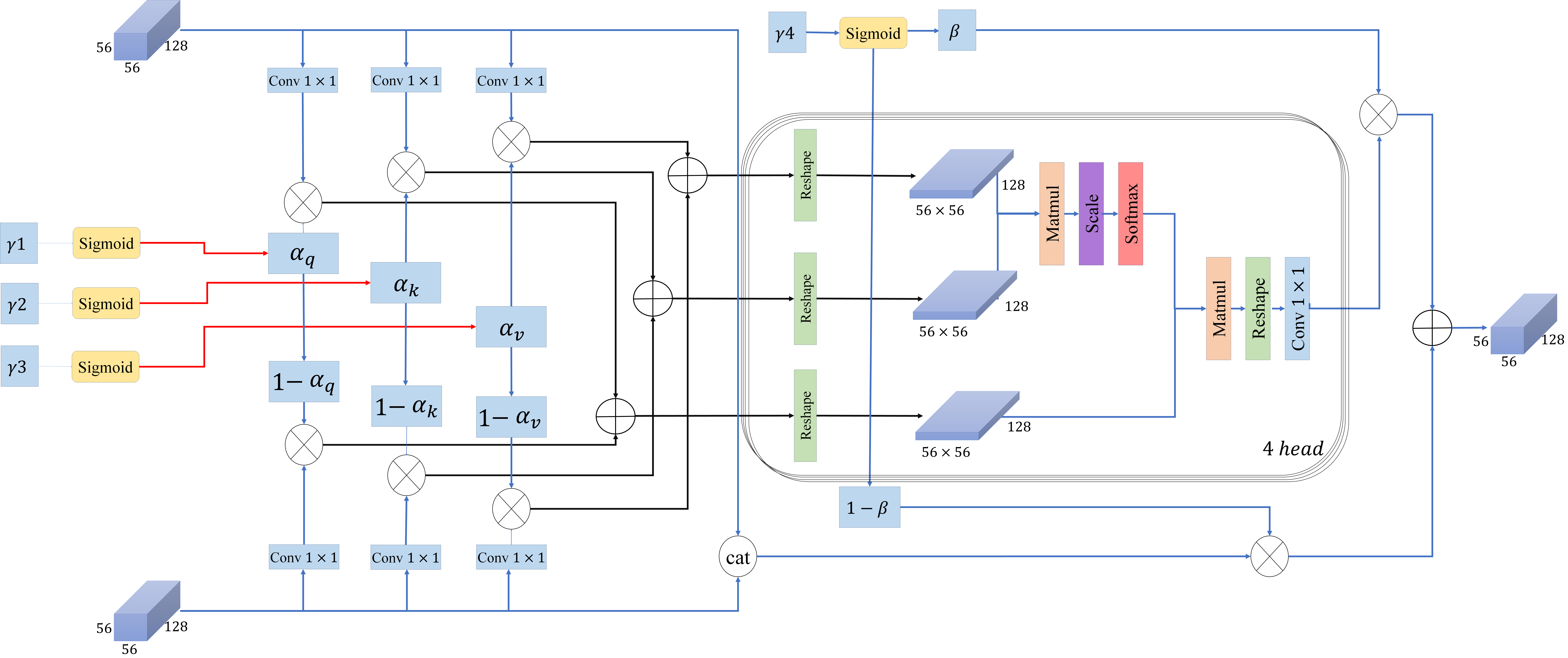
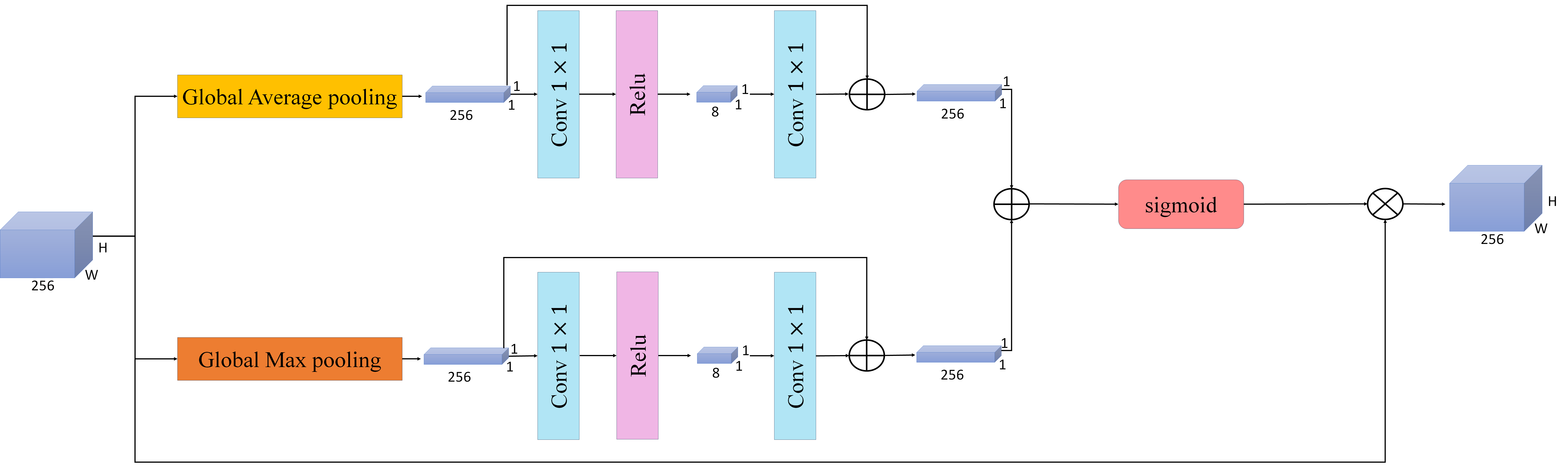
Lightweight Multi-Scale Framework for Human Pose and Action Classification
Paper
Code
We propose a lightweight modular attention-based architecture for human pose classification using a
Swin-Transformer backbone. The model integrates Spatial Attention, Context-Aware Channel Attention,
and a Dual Weighted Cross Attention module for effective multi-scale feature fusion.
Evaluated on Yoga-82 and Stanford 40 Actions datasets, it achieves high accuracy and outperforming state-of-the-art baselines,
with only 0.79 million parameters.